| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) | This complex organic chemical participates in many biological processes and is basically the the energy currency of life. It serves as the main energy source for metabolic functions, and it is responsible for storing and transporting chemical energy within cells. |
| Antiaging | Our bodies are made of millions of cells, which are strong, resilient, and and can easily replicate as an infant, child and young adult. As we get older, we age. From a biological standpoint, our body’s ability to generate new cells diminishes, and cell death occurs. Antiaging involves using tools and products that help delay, stop or reverse the natural aging process that occurs in humans. |
| Anti-inflammatory | The property of a substance or treatment that helps reduce signs of inflammation, such as swelling, tenderness, fever, and pain. |
| Biohacking | The art and science of changing the environment around you and inside you, so you have more control over your own biology, according to Dave Asprey, the creator of "biohacking". |
| Blood Circulation | The blood circulatory system (cardiovascular system) carries oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body, and returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart. The pumping action of the heart helps distribute nutrients and oxygen to your cells, and removes waste from the body. |
| Cellular Health | This refers to how well your cells -- including the proteins, mitochondria, and DNA inside of them — are functioning. If you have good cellular health, that means that your cells are able to repair and replicate themselves (in addition to carrying out their specialized functions). However, as we age over time, our cells are less apt, leading to a gradual accumulation of damage. Poor cellular health can affect your organs and put you at greater risk of experiencing some type of illness or disease. (Source) |
| Circadian Rhythm | A natural, biological process that regulates the sleep-wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours, like the rise and fall of the sun. Your body actually has several circadian rhythms happening throughout the day (and night), but when we refer to your body clock, we are speaking to your sleep/wake cycle that is largely influenced by light and temperature, and that in turn influences the rest of your body's smaller clocks. Learn more about circadian rhythms and health here.here. |
| Collagen | The most abundant protein (accounting for about 1/3) in the human body -- found in the bones, muscles, skin, and tendons -- that helps provide both strength and structure. Collagen also plays a role in replacing and restoring dead skin cells. As we age, we produce less collagen, and the structure of our skin naturally decline, leading to more wrinkles and lines. |
| Color Temperature | A way to describe the appearance of light, measured in Kelvin (K) on a scale from 1,000 to 10,000. Color temperatures over 5000 K are called "cool colors" and have a bluish appearance. Lower color temperatures (2700–3000 K) are called "warm colors", and they have a yellowish appearance. In this context, "warmth" is an indicator of radiated heat rather than temperature. (Source) |
| Cytochrome C Oxidase | An enzyme found in the mitochondria of bacteria, archaea, and in eukaryotes. It is responsible for catalyzing the final step in the mitochondrial electron transfer chain. Deficiency in the activity of cytochrome c oxidase has been associated with a wide range of human disorders, and is one of the most frequent causes of mitochondrial defects (NCBI). |
| Dermis | Also called corium, this is the thicker layer of skin that is located below the epidermis and above the superficial fascia. It is comprised of connective tissue, blood vessels, oil and sweat glands, nerves, hair follicles, and other structures. (NIH). |
| Detoxification | The metabolic process of removing toxic substances or qualities from the body. We are specifically interested in how light therapy can detoxify the body by increasing blood circulation and removing potentially carcinogenic heavy metals (like lead or mercury), as well as alcohol, nicotine, sodium, and sulfuric acid. This process can help relieve certain health symptoms, prevent illness, and increase overall vitality. |
| DNA | Short for deoxyribonucleic acid, DNA was first observed in 1869, but it wasn't until 1953 that researchers determined that its structure -- a double helix -- contains important biological information. This is basically the thing that makes you uniquely you, and all other organisms unique too. DNA is the hereditary genetic code that determines all characteristics of a living organism, and it is the primary component of the chromosomes found in cells. See: cellular health. Note: a 2017 study published found that random mistakes or mutations in DNA, (not heredity or environmental factors), accounts for two-thirds of cancer mutations in cells.(Source) |
| Drug-Free | All natural, not involving no administration of drugs of any kind. |
| Electromagnetic Spectrum | This refers to a continuum of all electromagnetic waves and their respective frequencies. This spectrum includes includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible) light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. |
| Energy Density | The amount of energy in a given mass (or volume). A good example of this is food; we measure the energy of food in calories. |
| Epidermis | The outermost layer of the skin that provides a waterproof barrier and creates our skin tone. This layer helps to protect us against water loss and from environmental pathenogens. It also regulates gas exchange and helps us absorb water and mineral nutrients. Within the epidermis are melanocytes -- cells that produce melanin -- which gives the skin its color. |
| FDA | Short for Food and Drug Administration. This organization is responsible for protecting the public health by assuring the safety, efficacy, and security of human and veterinary drugs, biological products, medical devices, our nation's food supply, cosmetics, and products that emit radiation. (USAGov) |
| Frequency (of a Wave) | The number of waves that pass a fixed point in a given amount of time, measured in hertz (Hz). |
| Hypodermis | The innermost (or deepest) and thickest layer of skin -- underneath the dermis and epidermis. It is also known as the subcutaneous layer or subcutaneous tissue. This layer contains fibroblasts, adipose tissue (fat cells), connective tissue, larger nerves and blood vessels, as well as macrophages, which are cells which are part of the immune system and help keep your body free of intruders. (VeryWell) |
| Inflammation | A biological response and defense mechanism in the body, in which the immune system recognizes damaged cells, irritants, and pathogens as a result of physical injury or an infection, and it begins the healing process. Symptoms of inflammation may vary depending on whether the reaction is acute or chronic. Pain, redness, immobility, heat, and swelling are considered acute inflammations specifically of the skin. It is possible to experience inflammation deep in your body, like in your organs; however, symptoms may not be as obvious. Chronic inflammation may result in: fatigue, mouth sore, chest pain, abdominal pain, fever, rashes, or joint pain. |
| Irradiance | Also known as power density. When using light therapy to heal the body, this is the amount of energy that the targeted part of your body receives while using the light. It is measured in milliwatts per square centimeter (mW/cm²). |
| LED Lighting | Short for light-emitting diode, an LED bulb emits visible light when an electrical current passes through it. |
| Light Spectrum | See Electromagnetic Spectrum. |
| Light Spectrum | See Electromagnetic Spectrum. |
| Light Therapy | Also known as photobiomodulation, phototherapy, or LLLT, this a painless, non-invasive form of treatment that uses specific wavelengths of light to help heal the skin and body. Different wavelengths notably have different purposes. This form of treatment was initially developed as a NASA technology, but has since become much more popular and affordable over the past decade. Studies have shown that 580nm (yellow light) has a shallow penetration level and is therefore appropriate for healing the surface of your skin -- think: scars, wrinkles, redness, inflammation, bruising. Wavelenghts 630nm and 660nm (red light), and 850nm (near-infrared light) have deeper penetration levels; these are ideal for healing your body all the way down to the bone -- think: muscle soreness or pain, post-surgery recovery, improved blood circulation. Learn more about light, light therapy, and your health here. |
| Lumens | A unit of measurement for the brightness of light in all directions. It is important for knowing how much light a single light source emits. One lumen per square meter is equal to one lux. |
| Lux |
Think of this as the "light per area". It is the basic unit of illuminance, which measures the total amount of light that falls on a particular surface. The total measurement can be the result of multiple light bulbs and even daylight mixed in.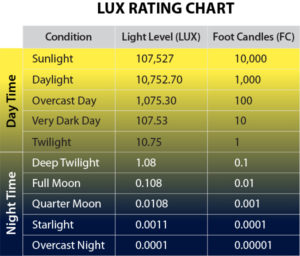
|
| Lymphatic System | A network of tissues and organs that help rid the body of toxins, waste and other unwanted materials. The primary function of the lymphatic system is to transport lymph, a fluid containing infection-fighting white blood cells, throughout the body. (Live Science |
| Mitochondria | Commonly known as the powerhouse of the cells in your body, mitochondria turn energy (ATP) into food and produce chemicals that help remove toxins from your cells to help keep you healthy. |
| Myoglobin | An oxygen-binding protein located primarily in muscles. It serves as a local oxygen reservoir that can temporarily provide oxygen when blood oxygen delivery is insufficient during periods of intense muscular activity (ScienceDirect). |
| Muscle Tissue | Soft tissue in the body composed of cells that have the ability to shorten or contract in order to produce movement of the body parts. Muscle tissue can be categorized into 3 different categories: skeletal muscle tissue, smooth muscle tissue, and cardiac muscle tissue. (NIH). Each type of muscle tissue in the human body has a unique structure and a specific role: - Skeletal muscle is composed of long cells (muscle fibers) that have a striated appearance. It moves bones and other structures by contracting and relaxing in response to voluntary messages from the nervous system. - Smooth muscle tissue is found in the walls of organs throughout the body (like the stomach and bladder) and provides elasticity, which allows these organs to expand and relax as needed to help facilitate bodily functions. - Cardiac muscle is specifically located in the heart's wall, it contracts the help the heart beat and pump blood. |
| Nanometer (NM) | A unit of measurement used to measure length -- especially that of microscopic objects, such as atomic structures or light wavelengths. |
| Near-Infrared (NIR) Light Therapy | Similar to red light therapy, except infrared energy is invisible to the human eye, and it penetrates the body deeper than red — reaching deep into soft tissues, muscles, joints, and bone. Since their wavelengths have deep penetration levels into the body, NIR can help stimulate cellular energy metabolism and increase energy production. Wavelengths 850nm and 880nm are thought to be the most effective within the NIR spectrum, and they can be used to help heal a variety of health conditions. |
| Nitric Oxide | A key molecule in the cardiovascular system which helps keep blood vessels healthy and regulate blood pressure. Nitric Oxide has also been found to be essential to the immune system and to the nervous system (including the brain) as well as integral with many chronic health conditions and diseases, such as chronic inflammation, erectile dysfunction, and cancer. This has led researchers to focus on nitric oxide as a potential target for medical therapies. A series of metabolic events occur with the releasing of nitric oxide when a light therapy device, such as TrueLight® emits 630nm, 660nm, and 850nm light wavelengths, which are easily absorbed by hemoglobin in the bloodstream and other body tissue. This release of nitric oxide dilates blood vessels and allows for greater cellular energy production. The result is in increased cellular activity that can promote healing, muscle recovery, and tissue strengthening. |
| Photobiomodulation | See Light Therapy. |
| Power Density | The amount of power in a given mass. It also describes the rate at which its energy within a system can be exhausted. If a system has a high power density, than it can output large amounts of energy based on its mass. Conversely, an object with a high energy density, but low power density can perform work for a relatively long period of time. For example, the power found in a mobile phone will last most of the day, but to recharge the device, it must be connected to another power source for an hour or more. (ResearchGate) |
| Red Light | Red (625-740 nm) is the color at the end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. Studies show that red light can be extremely effective for healing the body -- from the the surface of your skin all the way down to the bone. Specifically, 630nm and 660nm affect bodily cells on a biochemical level by increasing mitochondrial function – the ability to produce cellular energy. The more cellular energy production, the better the body functions as a whole. |
| Red Light Therapy | "A form of light therapy that works from the inside-out to enhance mitochondrial function in cells. When red light wavelengths are used on the skin’s surface, they can penetrate 8-10 millimeters into the skin. This, in turn, can have several benefits, including but not limited to: increased muscle recovery enhanced blood circulation increased collagen production reduced scars, wrinkles, & fine lines faster wound healing less pain anti-inflammatory effects" |
| RNA | Abbreviation for ribonucleic acid, it plays important roles in both normal cellular processes and diseases.The three most well-known and most commonly studied are messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), which are present in all organisms. More specifically, mRNA carries the protein blueprint from a cell's DNA to its ribosomes, which are the "machines" that drive protein synthesis. tRNA then carries the appropriate amino acids into the ribosome for inclusion in the new protein. Meanwhile, the ribosomes themselves consist largely of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules. (Nature) |
| Rosacea | A chronic, inflammatory skin condition that most often affects the face -- specifically with redness, swelling, and visible blood vessels. There is currently no cure, but light therapy can be used to help minimize symptoms. |
| Steady Mode | One of the available modes on any of our TrueLight light therapy devices. It involves the use of a steady light to penetrate and heal the body. When a single-frequency pulsed light hits the cells, it stimulates them to start producing more energy. As a result, the cells heals faster, and your body does too. |
| Stratum Corneum | The outermost layer of the epidermis within the skin. It serves as the primary barrier between the body and the environment. |
| Visible Light | The portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 390 to 700 nm. |
| Wattage | An amount of power, especially electric power, expressed in watts or kilowatts. |
| Watt | A unit of power that is defined as a derived unit of 1 joule per second, and is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. |
| Wavelength | The distance between two peaks in a wave. Different types of light have different wavelengths. The difference in wavelengths is the way we tell different kinds of electromagnetic energy apart. |
| Yellow Light | Yellow light is also sometimes referred to as amber light therapy. It encompasses the range of wavelengths from 570-620 nm. |
© 2024 TrueDark. All rights Reserved | Terms & Conditions | Privacy Policy | Cookie Policy